As we all know, although there were already diesel passenger cars in the 1930s, the development of early diesel cars originated from the unique fate of the Soviet T-34 tank during World War II. Be easy to fire and be the best on the battlefield. The current Chinese market is like the early international market. When consumers talk about diesel vehicles, they often laugh and say, "The biggest advantage of diesel vehicles is that they will not catch fire." However, with the development of diesel technology, people are increasingly discovering the infinite charm of diesel engines: high torque, long life, low fuel consumption, and low emissions. Diesel engines have become the most realistic and reliable means to solve automobile energy problems. Nowadays, every new car launched in Europe will be equipped with a diesel engine model, but in China, only FAW-Volkswagen may be able to achieve this move. But an indisputable reality is in front of us: with the energy crisis, the greenhouse effect is gradually increasing, and people's requirements for power are increasing. Although electronic fuel injection has been widely used, gasoline vehicles alone are not enough to solve these problems. question. So in the hinterland of the automobile industry - Germany has not stopped research on diesel engines for a moment. Even in China, there are only more than 10 models currently using diesel engines, including 5 passenger cars such as Jetta, Bora, Audi, Caddy, and JAC Refine, Foton Surf, Jiangling Landwind, Huatai Terraca, Shanghai Wanfeng, Liaoning Shuguang Wait for 5 SUVs. The 2.5-liter diesel engine on the Ruifeng diesel vehicle is imported from South Korea`s Hyundai Motor Company D4BH engine, and the 4 diesel passenger cars of FAW-Volkswagen all use the diesel engine cooperated by German Volkswagen and Bosch. These 5 diesel passenger cars are all pillars. Plug pump, pump nozzle technology.
The advantages of diesel engines are: fuel saving, environmental protection, strong power, economy, and easy maintenance. As long as the shortcomings are solved, there will be greater market prospects. The solution to realize electronically controlled diesel engines now seems to be a good solution. There are three technical roadmaps to realize diesel control, which are single pump, pump nozzle and high-pressure common rail. At present, major international auto parts suppliers are developing diesel common rail injection systems, such as: Bosch, Delphi, Siemens, Denso, VDO and Magna Marelli, which are the world's main suppliers of common rail injection systems At present, Bosch is the only company that produces common rail diesel injection systems in China. The three techniques are described below:
1. Unit pump technology
Delphi uses a single pump system on heavy vehicles. In terms of cost, when the domestic engine is upgraded from Euro II to Euro III, if the single pump is used, the engine changes are very small, and only the external camshaft box replaces the in-line pump of the Euro II engine. When upgrading from Euro Ⅲ to Euro Ⅳ, the main structure of the engine body remains unchanged. Just change the mechanical injector in the Euro Ⅲ system to Delphi's electronically controlled injector to form a double solenoid valve single pump system. Without major adjustments to the overall structure of the engine, the emission level of Euro IV can be reached. In terms of performance, the current pressure used by the domestic single pump reaches 200 MPa. When it is upgraded to Euro IV, the pressure can reach 250 MPa. A system consistency control similar to common rail I2C is used on the single pump to optimize the performance of the entire system. In terms of oil supply control, if the double solenoid valve unit pump system is used, not only the pressure can be controlled, but also the injection can be controlled, and multiple injections can also be used. It can meet Euro IV or Euro V standards. At present, Delphi's dual solenoid valve unit pump system is mass-produced in Europe, mainly for Euro IV standard engines, and Euro V standard engine related systems are under development.
Another advantage of the unitary pump system is its reliability and longevity. These performances have been proven in the European and North American markets by 10 or even 15 years of actual use and the use of millions of vehicles. The unit pump system can ensure low emissions and fuel consumption during engine use. At present, this very enhanced, very reliable performance and service life are still being further improved. Therefore, from Delphi's point of view, in terms of technology, it is believed that before 2010, most of the heavy-duty vehicle manufacturers in Europe and North America will adopt the unit pump system and pump nozzle technology. Delphi is also developing new systems required by new emissions regulations after 2010.
2. Pump nozzle technology
Excellent air mixture is the key factor to improve the power performance and fuel economy of the diesel engine and reduce the emission rate and noise rate. This requires the injection system to generate a sufficiently high injection pressure to ensure good fuel atomization, and at the same time must precisely control the fuel injection start point and fuel injection volume. The pump nozzle system can meet the above stringent requirements. Therefore, as early as 1905, Mr. Rudolf diesel, the founder of the diesel engine, proposed the concept of pump injector, envisaging the integration of fuel injection pump and nozzle, eliminating the need for high-pressure oil pipes and obtaining high injection pressure. Diesel engines with intermittently controlled pump injection systems have been used in ships and trucks since the 1950s. Afterwards, Volkswagen and Robert Bosh AG jointly developed a solenoid valve-controlled pump injection system for passenger cars. Pump
The main components are as follows:
(1) One-way valve: When the engine is not working, it prevents fuel from flowing back.
(2) Bypass valve: If there is air in the fuel, it will be discharged through here.
(3) Orifice and filter: to collect and separate air bubbles in the oil supply pipe.
(4) Pressure limiting valve 1: Open when the pressure in the oil supply pipe is adjusted to be greater than 0.75MPa.
(5) Pressure limiting valve 2: Keep the pressure in the oil return pipe at 0.10MPa.
(6) Fuel pump: The fuel pump is an intermittent vane pump, which has the advantage of supplying fuel even at lower engine speeds. The oil passage in the pump body keeps the oil pump rotor in a state of being soaked by fuel all the time, so that fuel can be delivered at any time.
(7) Fuel distribution pipe integration: The fuel distribution pipe is integrated in the oil supply pipe in the cylinder head, and its function is to distribute fuel to each pump nozzle in equal amounts. Here, the fuel is mixed with the heated fuel and forced to flow back to the supply pipe by the pump nozzle. tubing. Make the temperature of the fuel flowing in the fuel supply pipe to each cylinder consistent. All pump nozzles are supplied with the same amount of fuel to keep the engine running smoothly. Otherwise, the oil temperature of the pump nozzles will be different and the pump nozzles will be supplied with different qualities of fuel. This will make the engine run rough and create extremely high temperatures in the first few cylinders.
(8) Fuel cooling pump: to circulate the coolant in the cooling loop. When the fuel temperature reaches 70°C, the engine control unit switches it on through the fuel cooling pump relay.
Pump nozzles are used in many domestic passenger cars, such as Bora TDI, Touran TDI and Audi TDI. Compared with the previous technology (such as plunger pump), the pump nozzle technology has been significantly improved, and its biggest advantage is that the injection pressure is greatly increased, and the injection pressure of the turbocharger pump nozzle can reach more than 200MPa. Since the injection pressure directly affects the efficiency of diesel combustion, the combustion efficiency of the pump nozzle is very high.
3. High pressure common rail technology
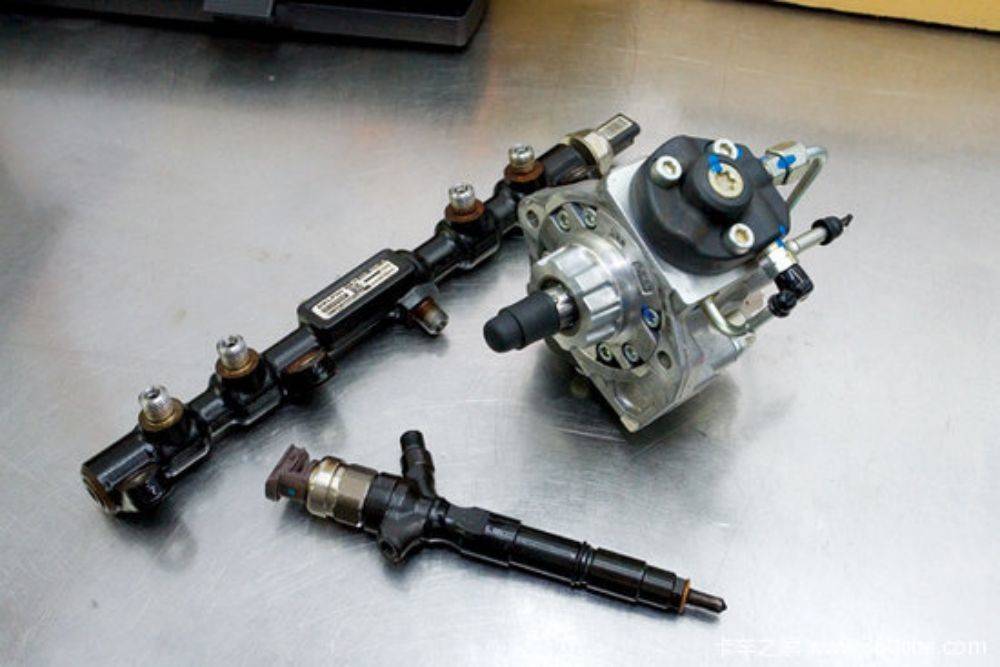
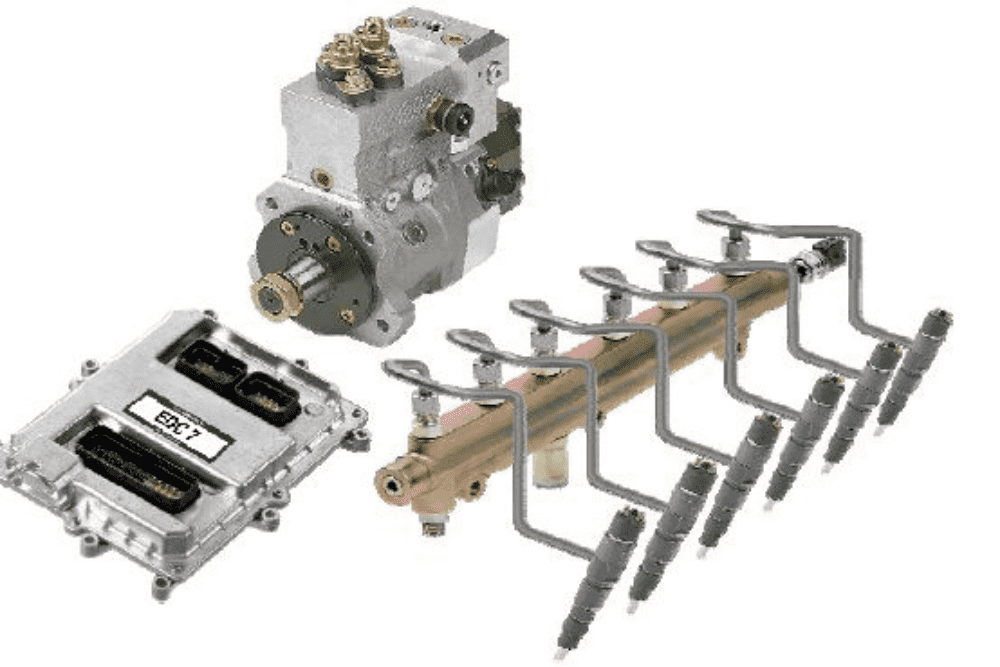
"CRDI" is the abbreviation of Common Rail Direct Injection in English, which means high-pressure common rail diesel direct injection technology, CRDI technology, SDI (naturally aspirated direct injection diesel engine) technology, TDI (direct injection turbocharged diesel engine) technology Diesel engine technology developed for Bosch in Germany. Common rail system consists of high pressure pump, fuel injection pipe, high pressure accumulator (common rail), fuel injector, electronic control unit, sensor and actuator.
The main contribution of the common rail fuel injection system is to completely separate the injection pressure generation and the injection process from each other. Through the precise control of the oil pressure in the common rail pipe, the pressure of the high pressure oil pipe has basically nothing to do with the engine speed. This innovation in diesel engine technology minimizes the vibration and noise of diesel engine models, while further reducing fuel consumption and making emissions cleaner. However, the fuel injection pressure of the common rail technology is lower than that of the pump nozzle system, which generally can only reach about 160MPa. Due to the wide adjustment of fuel injection pressure, diesel vehicles using common rail technology can better adapt to various working conditions, and it will not be difficult to start.
Bosch was the first passenger car to mass-produce the common rail fuel injection system in 1997. At that time, Bosch and Mercedes-Benz jointly launched the diesel Mercedes-Benz C-class car with common rail technology. At that time, Alfa Romeo 156 was also the first passenger car to use high-pressure common rail. one of the cars. Among domestic cars, Huatai Hyundai uses a common rail injection system. Diesel common rail system has been developed for 3 generations.
The first-generation common rail high-pressure pump always maintains the highest pressure, resulting in waste of fuel and high fuel temperature. The first-generation common rail system is designed for commercial vehicles, with a maximum injection pressure of 140MPa and a passenger vehicle injection pressure of 135MPa.
The second-generation common rail system can change the output pressure according to the engine demand, and has the functions of pre-injection and post-injection. Equipped with an oil pump to control the amount of oil, the injection pressure can reach 160MPa. Even at low pressures, the system provides just the right amount of fuel injection pressure for actual conditions. Not only does it help reduce fuel consumption, but it also reduces fuel temperature, thereby eliminating the need for fuel cooling. Pre-injection reduces engine noise: A small amount of fuel is injected into the cylinder for a millionth of a second prior to main injection, which pre-heats the combustion chamber on compression ignition. The preheated cylinder makes the compression ignition after the main injection easier, and the pressure and temperature in the cylinder no longer increase suddenly, which is beneficial to reduce the combustion noise. Post-injection is performed during the expansion process to generate secondary combustion, increase the temperature in the cylinder by 200-250°C, and reduce the hydrocarbons in the exhaust. Bosch's second-generation common rail system products have been tried on passenger cars such as Volvo's S60, V70D5 and BMW's 230d.
The third-generation common rail system has piezoelectric in-line injectors. In 2003, the third-generation common rail system came out, and the piezoelectric actuator of the piezoelectric (piezo) common rail system replaced the solenoid valve, thus obtaining more precise injection control. The oil return pipe is omitted, and the structure is simpler. The pressure can be adjusted elastically from 20 to 200MPa. The minimum injection volume can be controlled at 0.5mm3, reducing smoke and NOX emissions. The highest injection pressure reaches 180MPa. This system with newly developed piezoelectric in-line injectors enables a freer range of injection rate curves with pre-injection and post-injection.
Compared with other injection systems, the common rail system separates the pressure generation from the actual fuel injection process. The "rail" is used as a high-pressure accumulator, and its internal fuel pressure is always kept at the optimum pressure suitable for the specific working conditions of the engine. Common rail systems can be easily installed into various engines. In addition, the common rail system also provides a wider expansion function and more degrees of freedom in the design of the combustion process, which can make the diesel engine run with lower emissions, better fuel economy and low noise . The electronically controlled common rail system is an electronically controlled system that domestic experts agree is the highest level at present and will dominate in the future. The special design of the injector can implement flexible multiple injections, and the injection pressure can be adjusted arbitrarily under different speed and load conditions. The benefits brought to the engine are extremely ideal indicators. Due to these factors, electronically controlled common rail technology has been widely adopted for the new generation of passenger car diesel engines.